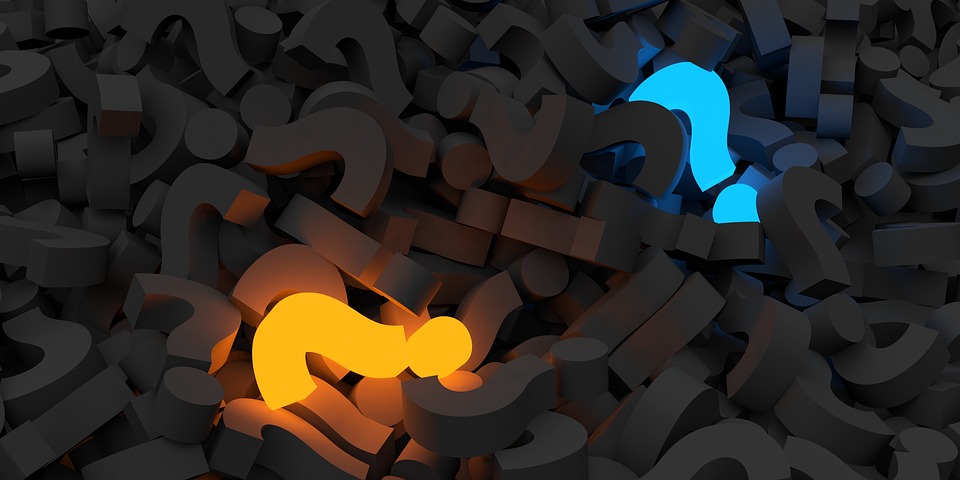


(5)When SRV-A sends ARP request looking for SRV-B, since the MAC Address information is in the local VEM table, the VEM will generate the ARP reply. (4) The VSM sends the mapping table to all VEMs with VTEPs in a particular VXLAN (3) The Virtual Supervisor Module (VSM) continuously aggregates the VXLAN VTEP local table information (2) The VEM adds the VM MAC Address information to the VXLAN VTEP local table. (1) When a new VM is instantiated in a VXLAN the hypervisor notifies the Virtual Ethernet Module (VEM).
In this section, we will describe the third mode: Enhanced VXLAN with ARP Termination. (3) Enhanced VXLAN with ARP Termination: MAC distribution done by VSM, unknown unicast dropped, ARP requests are handle locally at VEM (2) Enhanced VXLAN with MAC Distribution: MAC distribution done by VSM, unknown unicast dropped, ARP request replicated to every VTEP in a particular VXLAN (1) Enhanced VXLAN (unicast mode): VEM replicates BUM traffic every VTEP in a particular VXLAN The Nexus 1000v support three VXLAN unicast operation modes: VXLAN with Unicast Control Plane (Nexus 1000v) (8) Once the Mac Address information is learned, additional packets are Fed to the corresponding VTEP address. (7) VTEP1 will receive and de-encapsulate the packet and deliver it to SRV-A VTEP2 encapsulates the ARP reply with a VXLAN header and will unicast it to VTEP1. When SW2 VTEP2 receives it, it will lookup its local table and will find and entry with the information that traffic destined to SRV-A must be sent to VTEP1 address. (5) Each VTEP forwards the ARP request to its local destinations. (4) Each VTEP will receive and de-encapsulate the packet VXLAN packet and learn SRV-A Mac Address pointing to the remote VTEP address. (3) The multicast RP receive the packet and it will forward a copy to every VTEP that has joined the multicast group. (2) When the ARP request arrives to SW1 it will lookup its local table and if an entry is not found, it will encapsulate the ARP request over VXLAN and send it over the Multicast group configured for the specific VNI. SRV-A will generate an ARP request trying to discover SRV-B Mac Address. (1) Lets say SRV-A want to talk to SRV-B. Remote Mac Addresses are learn by a conversational Mac Address learning technique as follows (as per diagram): Initially, the switch will only learn the Mac Addresses of devices directly connected to them.

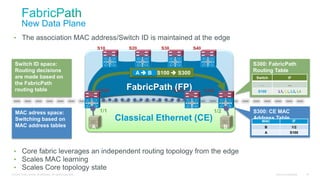
#CISCO MAC ADDRESS TABLE LEARNING MODE CONVERSATIONAL SERIES#
My focus is more towards the Nexus 7k, Nexus 9k, Nexus 1k and CSR1000v.Įach control plane may have a series of caveats in their own, but those are not covered by this blog entry. This post tries to summarize the three (3) control planes currently supported by some of the Cisco NX-OS/IOS-XR. It is implemented and supported by multiple vendors and it is even natively supported in server OS like the Linux Kernel. The most commonly use VXLAN control plane is multicast. There are several drafts describing the use of different control planes. The standard does not define a “standard” control plane for VXLAN. That is where the evolution of VXLAN control plane comes into play. Now, as with any other overlay network protocol, its scalability is tied into how well it can handle the Broadcast, Unknown unicast and Multicast (BUM). One of the Layer2 over Layer3 (or Layer2 over UDP) protocols adopted by the industry is VXLAN. With the adoption of overlay networks as the standard deployment for multi-tenant network, Layer2 over Layer3 protocols have been the favorite among network engineers.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
